Rustic Ambience
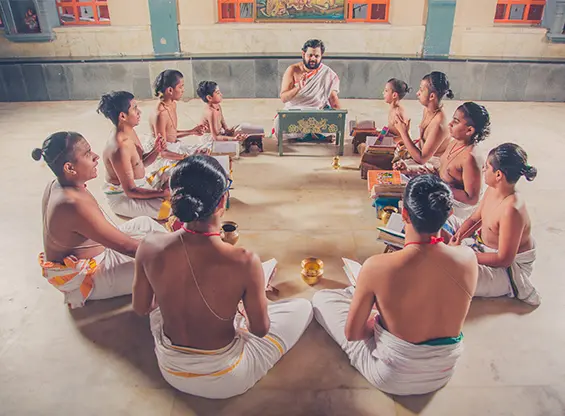
The Vedapatashala is usually abuzz with cheerful children, has on its campus a play area, dormitory, etc. The rustic ambience is perfect for the quiet service being rendered on the institutions grounds.
The Vedas are the core of the Sanatana Vaidecai Hindu tradition. Veda Patashala was established for the study of the scriptures in the traditional Gurukula system. Veda Patashala’s mission is protect the Vedas and continue its propagation.
The Vedas are a large body of religious texts composed in Vedic Sanskrit. The texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit knowledge and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. The Vedasare considered to be anaadi, without a beginning. This implies that it has existed since the beginning of time. Hindus also consider the Vedas to be apaourusheya which means of non-human origin. It is believed that Eshwara, God did not create the Vedas,and that the Vedas have existed since the existence of Eshwara. This implies that they are one and the same.
The Sanskrit word ‘Veda’, means knowledge. The Vedas are also referred to by some as Shruthi, that which is heard. It is believed that the sounds of the Vedas always surround us and that Rishis received the Vedas once they were properly attuned to it. The Vedas were always passed on via word of mouth from Guru to Shishya. This vast knowledge was divided by the great Veda Vayasa into four. They are Rig Veda, Yajur Veda, Sama Veda and Atharva Veda. The final part of all these four Vedas is the Upanishads. The Upanishads are also known as Vedanta.
Learning the Vedas and practicing the teachings involves the entire body. Thus, Vedas are believed to have organs,the Vedaangas. There are six Vedaangas. Siksha - the nose or lungs of the Veda Purusha , Vyakarana - the mouth or grammar of the Veda Purusha, Chandas the feet of the Veda Purusha, Niruktam - the ears of the Veda Purusha, Jyotisha - the eyes and Kalpa the arms of the Veda Purusha.
Out of the 14 Vidyas, 4 are Vedas, the 6 Vedaangas the remaining 4 are Upaangas, subsidiary or secondary limbs. These are Meemaasa, Nyaaya, Puraana and Dharma Saastra.


The Vedas are a large body of religious texts originating in ancient India. Composed inVedic Sanskrit, the texts constitute the oldest layer of Sanskrit literature and the oldest scriptures of Hinduism. Hindus consider the Vedas to be apaurueya, which means "not of a man, superhuman impersonal, authorless"
The Sanskrit word, veda, means "knowledge." The Vedas are also referred to by some as sruti literature, meaning “what is heard,” as opposed to other sacred smrti texts, meaning “what is remembered." In this way, they are considered to be the direct word of the Divine.
The four books, or texts, of the Vedas are the "Rig Veda" (which is the oldest), the "Yajur Veda," the "Sama Veda" and the "Atharva Veda."
The Rig Veda is a collection of inspired songs or hymns and is a main source of information on the Rig Vedic civilization.
The Yajur Veda is also a liturgical collection and was made to meet the demands of a ceremonial religion. The Yajur Veda practically served as a guidebook for the priests who execute sacrificial acts muttering simultaneously the prose prayers and the sacrificial formulae (yajus).
The Sama Veda is purely a liturgical collection of melodies (saman). The hynms in the Sama Veda, used as a musical notes, were almost completely drawn from the Rig Veda and have no distinctive lessons of their own.
The last of the Vedas, this is completely different from the other three Vedas. It concentrates on the material needs of the society. Its hymns are of a more diverse character than the Rig Veda and are also simpler in language. In fact, many scholars do not consider it part of the Vedas at all.

Total Students

Overall Staffs
Successful Batches
Gohshala

The Vedapatashala is usually abuzz with cheerful children, has on its campus a play area, dormitory, etc. The rustic ambience is perfect for the quiet service being rendered on the institutions grounds.

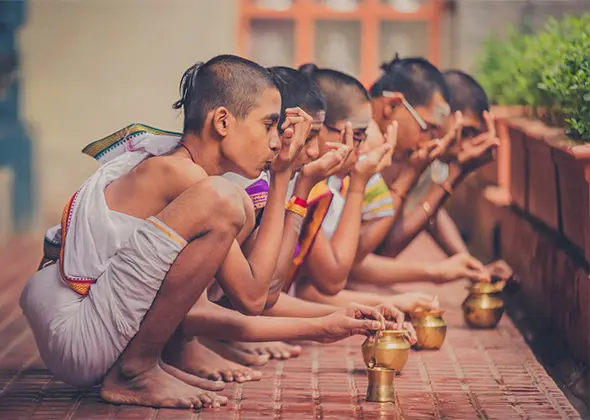
At the Vedapatashala the students learn yoga, meditation, Vedic chanting, reading of scriptures, mathematics, seva and special programs designed to infuse their lives with essential values and ethics.
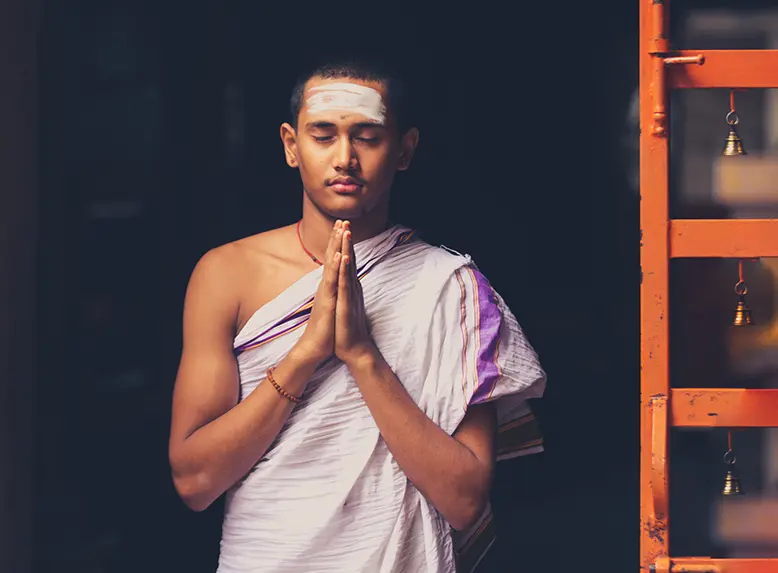

Every Week, Surya Namaskar Parayanam is performed on a particular day; and the students are actively encouraged to develop cultural and fine arts talents at the Patashala.

Every Week, Surya Namaskar Parayanam is performed on a particular day; and the students are actively encouraged to develop cultural and fine arts talents at the Patashala.



